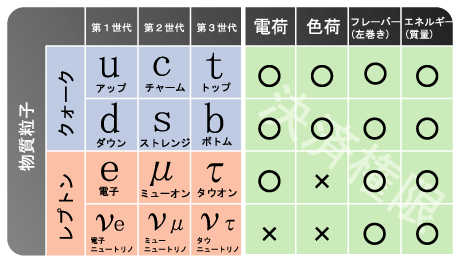
22 Quantum Field Theory #universe #quantum22-1 What is Quantum Field?○Space is quantum fields, particle is the excited quantum field.※Vacuum (nothing condition) is the quantum fields where the energy is the lowest.○In quantum field theory, we consider particles(Material fields)as harmonic oscillators and quantize them. Then, as a system of infinite number of harmonic oscillators, the theory is assembled.※The motion of an object that is connected to a spring and vibrates is called "harmonic oscillation".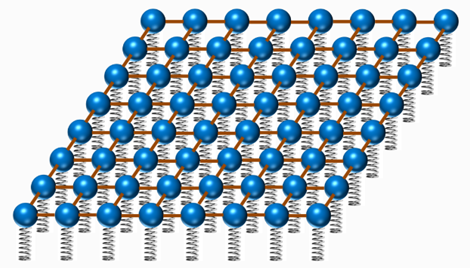 ※Image of Quantum field [1]○Quantum field theory combines special relativity theory and quantum mechanics.・・・The difference between special and general relativity is gravity only. In the world of elementary particles, since the mass is small, the work of gravity is equivalent to almost completely nothing compared to other forces.○Quantum mechanics is an approximate form of quantum field theory limited to the low energy state.・Quantum mechanics can not be used for phenomena in which the number of particles changes such as particle generation and extinction.○Prior to the emergence of string theory, the theory describing the smallest scale was quantum field theory.22-2 Field types and particles1)Gauge field and gauge particle (force mediating particle)Electromagnetic field ・・・PhotonWeak interaction (causing β decay of neutrons) • • • W boson, Z boson Strong interaction(Power to combine quarks)・・・Gluon Gravitational field・・・Graviton※ Gauge theory(3 + 1 dimension) is the theory underlying the Standard Model.※As a method to describe gravity, there is a method based on Newton's theory of gravity and general relativity.※The state with the lowest energy of the string is the gauge particle. ← Superstring Theory2)Material field and material particles
※Image of Quantum field [1]○Quantum field theory combines special relativity theory and quantum mechanics.・・・The difference between special and general relativity is gravity only. In the world of elementary particles, since the mass is small, the work of gravity is equivalent to almost completely nothing compared to other forces.○Quantum mechanics is an approximate form of quantum field theory limited to the low energy state.・Quantum mechanics can not be used for phenomena in which the number of particles changes such as particle generation and extinction.○Prior to the emergence of string theory, the theory describing the smallest scale was quantum field theory.22-2 Field types and particles1)Gauge field and gauge particle (force mediating particle)Electromagnetic field ・・・PhotonWeak interaction (causing β decay of neutrons) • • • W boson, Z boson Strong interaction(Power to combine quarks)・・・Gluon Gravitational field・・・Graviton※ Gauge theory(3 + 1 dimension) is the theory underlying the Standard Model.※As a method to describe gravity, there is a method based on Newton's theory of gravity and general relativity.※The state with the lowest energy of the string is the gauge particle. ← Superstring Theory2)Material field and material particles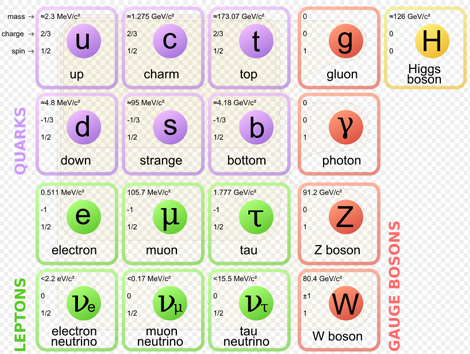 ※Under the "quarks and leptons" definition, the elementary and composite particles made of the quarks (in purple) and leptons (in green) would be matter—while the gauge bosons (in red) would not be matter. However, interaction energy inherent to composite particles (for example, gluons involved in neutrons and protons) contribute to the mass of ordinary matter. [2]3)Higgs field (scalar field) and Higgs particle・・・Boson →No.2422-3 その他○Quantum field theory is the fundamental theory of particle physics (describing behavior of elementary particles), nuclear physics, condensed matter physics (describing multi-body theory effects such as critical phenomena and phase transitions).【References】1. Brian Skinner”A Children’s Picture-book Introduction to Quantum Field Theory” 201508202.Matter - Wikipedia
※Under the "quarks and leptons" definition, the elementary and composite particles made of the quarks (in purple) and leptons (in green) would be matter—while the gauge bosons (in red) would not be matter. However, interaction energy inherent to composite particles (for example, gluons involved in neutrons and protons) contribute to the mass of ordinary matter. [2]3)Higgs field (scalar field) and Higgs particle・・・Boson →No.2422-3 その他○Quantum field theory is the fundamental theory of particle physics (describing behavior of elementary particles), nuclear physics, condensed matter physics (describing multi-body theory effects such as critical phenomena and phase transitions).【References】1. Brian Skinner”A Children’s Picture-book Introduction to Quantum Field Theory” 201508202.Matter - Wikipedia
21 Quantum Cosmology #universe #cosmology21-1 The Birth of the universe:Quantum fluctuation [1] [2]・In modern physics, there is no such thing as perfect nothing. ・Vacuum or empty space has Vacuum energy and tension.・In quantum level, even in a vacuum, pairs of matter and anti-matter particles are constantly being created and annihilated. ・The universe was born by the rapid expansion of the quantum fluctuation. ※Vacuum fluctuations [3]※The problem remains.・・・ What is the vacuum energy? 21-2 Inflation cosmology [4]・・・1981 Katsuhiko Sato, Alan Guth ・The theory is that the universe is the magnitude of 10^24-th power(=Inflation) in the period from after 10 minus 36 square seconds immediately after birth until after 10 minus 34 square seconds by the phase transition of space due to the Quantum tunneling of vacuum energy.※The size of the universe (10^-27m) is much smaller than atom (10^-10m).⇒3 millimeters (10^-3m)※The inflation rate is 60-fold of light speed.○The driving force behind this inflation has been said that the energy that was released during the phase transition of the vacuum. [5]○In early inflationary models, the phase transition of the vacuum was considered that it is generated by the Quantum tunnelling or tunnel effect. However, in a model named new inflation or slow-roll inflation, instead of tunneling out of a false vacuum state, inflation is considered that occurred by rolling down a potential energy hill. [5]※Quantum tunnelling or tunneling refers to the quantum mechanical phenomenon where a particle tunnels through a barrier that it classicallycould not surmount. It has important applications to modern devices such as the tunnel diode,[2] quantum computing, and the scanning tunnelling microscope. [6]※Nuclear fusion is also thanks to the tunnel effect. Without the tunnel effect the sun can not shine. [7]・Huge energy is converted into heat. And it will be the whole universe to the ultra high. ⇒ Big Bang
※Vacuum fluctuations [3]※The problem remains.・・・ What is the vacuum energy? 21-2 Inflation cosmology [4]・・・1981 Katsuhiko Sato, Alan Guth ・The theory is that the universe is the magnitude of 10^24-th power(=Inflation) in the period from after 10 minus 36 square seconds immediately after birth until after 10 minus 34 square seconds by the phase transition of space due to the Quantum tunneling of vacuum energy.※The size of the universe (10^-27m) is much smaller than atom (10^-10m).⇒3 millimeters (10^-3m)※The inflation rate is 60-fold of light speed.○The driving force behind this inflation has been said that the energy that was released during the phase transition of the vacuum. [5]○In early inflationary models, the phase transition of the vacuum was considered that it is generated by the Quantum tunnelling or tunnel effect. However, in a model named new inflation or slow-roll inflation, instead of tunneling out of a false vacuum state, inflation is considered that occurred by rolling down a potential energy hill. [5]※Quantum tunnelling or tunneling refers to the quantum mechanical phenomenon where a particle tunnels through a barrier that it classicallycould not surmount. It has important applications to modern devices such as the tunnel diode,[2] quantum computing, and the scanning tunnelling microscope. [6]※Nuclear fusion is also thanks to the tunnel effect. Without the tunnel effect the sun can not shine. [7]・Huge energy is converted into heat. And it will be the whole universe to the ultra high. ⇒ Big Bang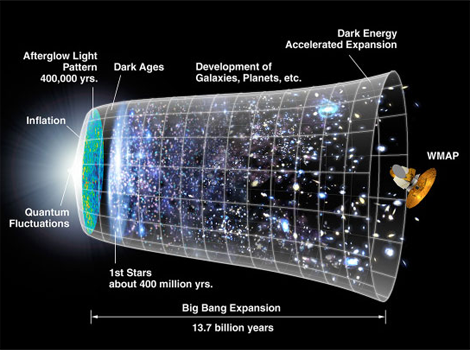 • By inflation, some of the problems of big bang cosmology, which has been pointed out in the 1970s is resolved. [4](The problems of big bang cosmology )1-That the universe is observed is very flat. (Flatness problem)2 -The universe is extremely uniform. (Horizon problem)3-Phase defect of space in which exist in many models of grand unified theory (GUT) has been predicted is not observed at all. (Monopole problem)<Problems and observation> ・Driving force of the secondary inflation that began before several billion years (4 ~ 6 billion years) remains as unresolved issues. [8]・Precision exploration of gravity waves is planned by such as Planck(cosmic microwave background radiation observation satellites of the European Space Agency (ESA) ) or the South Pole satellite. [8]・In February 2016, the Advanced LIGO team announced that they had detected gravitational waves from a pair of black holes merging. [9]・Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo starts the observation of gravitational waves in 2017 by the underground telescope "KAGRA".・In the 2021 fiscal year, Japan plans to launch the artificial satellite "Light Bird" which is possible all-sky observation with high degree accuracy.21-3 Free lunch model(Alan Harvey Guth)[8]・・・1988 ・Matter and radiation can have not only "positive" energy but also "negative" energy.・Negative energy is repulsive force, and repulsive force inflates the space.・When "negative" energy is generated by quantum fluctuations, "positive" energy of the same amount is also generated.• Thus, in the closed universe, material and radiation is filled accoding to the expansion!・This is perfectly consistent with the Law of Conservation of Energy, so the Expansion of the universe is the ultimate Free lunch.・Guth’s model is believed to explain the cosmological constant of General relativity.21-4 The Big Bang model [10]・・・1948 George GamowThe model is assumed that the Universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state.・The Big Bang model is explained by Cosmology based on theory of elementary particles.・Elementary particles are explained by several kinds of symmetry in theory of elementary particles.・Although it is assumed that there is an equivalent amount of matter and antimatter in the universe from this, there is not much antimatter to be found. Something must have happened to tip the balance. ・One of the greatest challenges in physics is to figure out matter and antimatter asymmetry.☆My ideaSince the fundamental power of antimatter is repulsive force, it is thought that antimatter was diffused at high speed rather than the substance after separation of gravity and antigravity (10E-44(ten to the minus 44th) second after the Big Bang).【References】1. No.16 Uncertainty Principle2. Jeff Miller, Ph.D.” Can Quantum Mechanics Produce a Universe from Nothing?”3. RevoScience”Young researcher proposes new explaination for unsolved problems in physics…”4. Wikipedia:Inflation(cosmology)5. No.16-3 Phase Transitions of Vacuum /Inflation Cosmology/Quantum Tunneling6. Wikipedia:Quantum tunnelling7. Masahiro Maeno “Introduction to Quantum mechanics(Japanese) " 20060216 (p.107) 8.A Universe from Nothing. Lawrence M. Krauss -20129. Wikipedia:Gravitational wave10. No.18 The Big Bang model
• By inflation, some of the problems of big bang cosmology, which has been pointed out in the 1970s is resolved. [4](The problems of big bang cosmology )1-That the universe is observed is very flat. (Flatness problem)2 -The universe is extremely uniform. (Horizon problem)3-Phase defect of space in which exist in many models of grand unified theory (GUT) has been predicted is not observed at all. (Monopole problem)<Problems and observation> ・Driving force of the secondary inflation that began before several billion years (4 ~ 6 billion years) remains as unresolved issues. [8]・Precision exploration of gravity waves is planned by such as Planck(cosmic microwave background radiation observation satellites of the European Space Agency (ESA) ) or the South Pole satellite. [8]・In February 2016, the Advanced LIGO team announced that they had detected gravitational waves from a pair of black holes merging. [9]・Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo starts the observation of gravitational waves in 2017 by the underground telescope "KAGRA".・In the 2021 fiscal year, Japan plans to launch the artificial satellite "Light Bird" which is possible all-sky observation with high degree accuracy.21-3 Free lunch model(Alan Harvey Guth)[8]・・・1988 ・Matter and radiation can have not only "positive" energy but also "negative" energy.・Negative energy is repulsive force, and repulsive force inflates the space.・When "negative" energy is generated by quantum fluctuations, "positive" energy of the same amount is also generated.• Thus, in the closed universe, material and radiation is filled accoding to the expansion!・This is perfectly consistent with the Law of Conservation of Energy, so the Expansion of the universe is the ultimate Free lunch.・Guth’s model is believed to explain the cosmological constant of General relativity.21-4 The Big Bang model [10]・・・1948 George GamowThe model is assumed that the Universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state.・The Big Bang model is explained by Cosmology based on theory of elementary particles.・Elementary particles are explained by several kinds of symmetry in theory of elementary particles.・Although it is assumed that there is an equivalent amount of matter and antimatter in the universe from this, there is not much antimatter to be found. Something must have happened to tip the balance. ・One of the greatest challenges in physics is to figure out matter and antimatter asymmetry.☆My ideaSince the fundamental power of antimatter is repulsive force, it is thought that antimatter was diffused at high speed rather than the substance after separation of gravity and antigravity (10E-44(ten to the minus 44th) second after the Big Bang).【References】1. No.16 Uncertainty Principle2. Jeff Miller, Ph.D.” Can Quantum Mechanics Produce a Universe from Nothing?”3. RevoScience”Young researcher proposes new explaination for unsolved problems in physics…”4. Wikipedia:Inflation(cosmology)5. No.16-3 Phase Transitions of Vacuum /Inflation Cosmology/Quantum Tunneling6. Wikipedia:Quantum tunnelling7. Masahiro Maeno “Introduction to Quantum mechanics(Japanese) " 20060216 (p.107) 8.A Universe from Nothing. Lawrence M. Krauss -20129. Wikipedia:Gravitational wave10. No.18 The Big Bang model
21 素粒子論的宇宙論 #宇宙 #宇宙論21-1 宇宙の誕生:量子的ゆらぎ[1] [2]・現代物理学では、完全な無は存在しない。・真空若しくは空っぽの空間は真空エネルギーと力を持つ。・量子的レベルでは、真空であっても、物質(素粒子)と反物質の粒子のペアが生成と消滅を繰り返している。・宇宙は量子的ゆらぎからの急速な膨張により誕生した。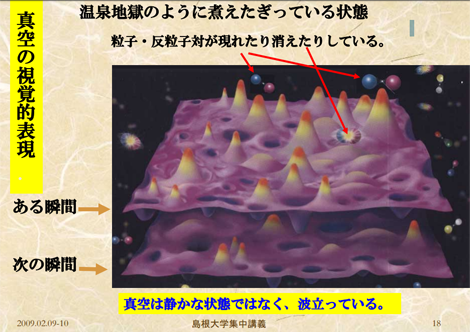 図:真空のゆらぎ [3]※問題が残る。・・・その真空エネルギーはどこから来たのか?21-2 インフレーション理論 [4]・・・1981年 佐藤勝彦、アラン・グース○宇宙は誕生直後の10のマイナス36乗秒後から10のマイナス34乗秒後までの間に真空エネルギーのトンネル効果(※)により、空間が相転移し、その大きさが10の24乗倍に膨張(=インフレーション的膨張)したとする理論。※原子(10^-10m)よりはるかに小さい実宇宙(10^-27m)⇒3ミリ程度(10^-3m)※膨張速度は光速の60倍超○インフレーションの原動力となったのは、真空の相転移の際に解放されたエネルギーだとされている。[5]○初期のインフレーション理論(古いインフレーション)では、偽の真空と真の真空の間に明確なポテンシャルの障壁があり、それをトンネル効果によって乗り越えることで真空の相転移が発生すると考えられていたが、後に述べられたインフレーション理論(ゆっくり転がるインフレーション)では、明確なポテンシャルの障壁はなく、偽の真空から真の真空へと至る緩やかなポテンシャルの坂があるとされている。[5]※トンネル効果:エネルギーの壁を、あたかもトンネルを掘ったかのようにそれより低いエネルギーを持った粒子が通り抜けてしまう現象。半導体はこの原理を利用してつくられている。[6]※核融合もトンネル効果のおかげ。トンネル効果がなければ太陽は輝くことはできない。[7]・インフレーションにより生じた巨大なエネルギーは熱に変わって宇宙全体を超高音にする。⇒ビッグバン
図:真空のゆらぎ [3]※問題が残る。・・・その真空エネルギーはどこから来たのか?21-2 インフレーション理論 [4]・・・1981年 佐藤勝彦、アラン・グース○宇宙は誕生直後の10のマイナス36乗秒後から10のマイナス34乗秒後までの間に真空エネルギーのトンネル効果(※)により、空間が相転移し、その大きさが10の24乗倍に膨張(=インフレーション的膨張)したとする理論。※原子(10^-10m)よりはるかに小さい実宇宙(10^-27m)⇒3ミリ程度(10^-3m)※膨張速度は光速の60倍超○インフレーションの原動力となったのは、真空の相転移の際に解放されたエネルギーだとされている。[5]○初期のインフレーション理論(古いインフレーション)では、偽の真空と真の真空の間に明確なポテンシャルの障壁があり、それをトンネル効果によって乗り越えることで真空の相転移が発生すると考えられていたが、後に述べられたインフレーション理論(ゆっくり転がるインフレーション)では、明確なポテンシャルの障壁はなく、偽の真空から真の真空へと至る緩やかなポテンシャルの坂があるとされている。[5]※トンネル効果:エネルギーの壁を、あたかもトンネルを掘ったかのようにそれより低いエネルギーを持った粒子が通り抜けてしまう現象。半導体はこの原理を利用してつくられている。[6]※核融合もトンネル効果のおかげ。トンネル効果がなければ太陽は輝くことはできない。[7]・インフレーションにより生じた巨大なエネルギーは熱に変わって宇宙全体を超高音にする。⇒ビッグバン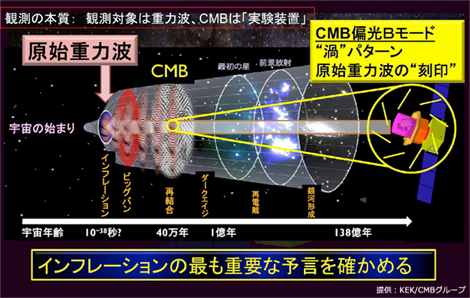 ※インフレーションのイメージ[8]・インフレーション理論によって、1970年代に指摘されていたビッグバン理論のいくつかの問題点が解決される。[4][9] 1)観測される宇宙が極めて平坦であること(平坦性問題)2)宇宙が極めて一様であること(地平線問題)3)多くの大統一理論 (GUT) のモデルで存在が予言されている空間の位相欠陥が全く観測されないこと(モノポール問題)<課題と観測>・数十億年(40億年~60億年)前に始まったとする第2次インフレーションの原動力が未解決の問題として残っている。[10]・今後は、欧州宇宙機関(ESA)の宇宙マイクロ波背景放射観測衛星プランクや南極点衛星などによって、重力波の更なる精密探査が行われる事によって、この未解決の問題についての一定の見解が得られるのではないか?と期待がもたれている。[10]・2015年 カリフォルニア工科大とマサチューセッツ工科大などの共同研究チームが重力波を初検出。[11]・東大宇宙線研究所などは岐阜県飛騨市に建設中の地下望遠鏡「KAGRA(かぐら)」で2017年度に重力波の観測を開始予定。・日本は高精度で全天観測が可能な人工衛星「ライトバード」を2021年度にも打ち上げる予定。・NASAのジェット推進研究所およびESAでは、2035年に、宇宙重力波望遠鏡(Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA):レーザー干渉計)を使って並行宇宙の重力を観測する予定。[12][13]21-3 フリーランチ・モデル[10]・・・1988年 アラン・グースのフリーランチ・モデル・物質や放射は「正の」エネルギーだけでなく、「負の」エネルギーも持つことができる。・負のエネルギーは斥力であり、空間を膨張させる。・量子ゆらぎにより「負の」エネルギーを持つものが生成されると、そのエネルギーと釣り合う「正の」エネルギーも生成する。・つまり、閉じられた宇宙においては、宇宙の膨張に伴い物質と放射が充てんされる! ・これは、エネルギー保存則と完全に一致しており、宇宙は究極のフリーランチ!・グースのモデルは、一般相対性理論の宇宙定数を説明するものと考えられている。21-4 ビッグバン理論 [14]・・・1948年 ガモフ・ビッグバン理論:「この宇宙には始まりがあって、爆発のように膨張して現在のようになった」とする説・ビッグバン理論は素粒子論的な宇宙論で説明された。・素粒子論の基本原理では、素粒子は数種類の対称性で説明される。・このことから宇宙には物質と反物質が同じ量あると想定されるが、反物質は観測されることは稀である。・ビッグバンでは物質と反物質が同じだけできたが、その反物質をニュートリノがほんの少しだけつまみ取るようにして、物質に変えたという考えもある。[15]・宇宙における物質の存在という非対称性(反物質がほとんどないということ)は、素粒子論におけるひとつの謎とされている。☆考察反物質の基本的な力は斥力であることから、重力・反重力の分離後(ビッグバンから10のマイナス44乗秒後)、反物質は物質よりも高速で拡散したと考えられる。【参 考】1. No.16 不確定性原理2.Jeff Miller, Ph.D.” Can Quantum Mechanics Produce a Universe from Nothing?”http://www.apologeticspress.org/apcontent.aspx?category=12&article=45843. 島根大学集中講義 真空の性質20094.Wikipedia:宇宙のインフレーション5. No.16-3 真空の相転移・インフレーション宇宙・トンネル効果6.Wikipedia:トンネル効果7. 前野昌弘 “量子力学入門" 20060216 (p.107) 8.三菱電機”宇宙創生時の急膨脹「インフレーション」の証拠写真を撮る日”9.「気が遠くなる未来の宇宙のはなし」佐藤勝彦(2013年刊)10.「宇宙が始まる前には何があったのか?」ローレンス・クラウス(2013年11月刊)11. 産経新聞 2016021212.Wikipedia:宇宙重力波望遠鏡13. LISA Project Office14.No.18 ビッグバン・モデル15.「宇宙は何でできているのか」村山 斉 (p.215)
※インフレーションのイメージ[8]・インフレーション理論によって、1970年代に指摘されていたビッグバン理論のいくつかの問題点が解決される。[4][9] 1)観測される宇宙が極めて平坦であること(平坦性問題)2)宇宙が極めて一様であること(地平線問題)3)多くの大統一理論 (GUT) のモデルで存在が予言されている空間の位相欠陥が全く観測されないこと(モノポール問題)<課題と観測>・数十億年(40億年~60億年)前に始まったとする第2次インフレーションの原動力が未解決の問題として残っている。[10]・今後は、欧州宇宙機関(ESA)の宇宙マイクロ波背景放射観測衛星プランクや南極点衛星などによって、重力波の更なる精密探査が行われる事によって、この未解決の問題についての一定の見解が得られるのではないか?と期待がもたれている。[10]・2015年 カリフォルニア工科大とマサチューセッツ工科大などの共同研究チームが重力波を初検出。[11]・東大宇宙線研究所などは岐阜県飛騨市に建設中の地下望遠鏡「KAGRA(かぐら)」で2017年度に重力波の観測を開始予定。・日本は高精度で全天観測が可能な人工衛星「ライトバード」を2021年度にも打ち上げる予定。・NASAのジェット推進研究所およびESAでは、2035年に、宇宙重力波望遠鏡(Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA):レーザー干渉計)を使って並行宇宙の重力を観測する予定。[12][13]21-3 フリーランチ・モデル[10]・・・1988年 アラン・グースのフリーランチ・モデル・物質や放射は「正の」エネルギーだけでなく、「負の」エネルギーも持つことができる。・負のエネルギーは斥力であり、空間を膨張させる。・量子ゆらぎにより「負の」エネルギーを持つものが生成されると、そのエネルギーと釣り合う「正の」エネルギーも生成する。・つまり、閉じられた宇宙においては、宇宙の膨張に伴い物質と放射が充てんされる! ・これは、エネルギー保存則と完全に一致しており、宇宙は究極のフリーランチ!・グースのモデルは、一般相対性理論の宇宙定数を説明するものと考えられている。21-4 ビッグバン理論 [14]・・・1948年 ガモフ・ビッグバン理論:「この宇宙には始まりがあって、爆発のように膨張して現在のようになった」とする説・ビッグバン理論は素粒子論的な宇宙論で説明された。・素粒子論の基本原理では、素粒子は数種類の対称性で説明される。・このことから宇宙には物質と反物質が同じ量あると想定されるが、反物質は観測されることは稀である。・ビッグバンでは物質と反物質が同じだけできたが、その反物質をニュートリノがほんの少しだけつまみ取るようにして、物質に変えたという考えもある。[15]・宇宙における物質の存在という非対称性(反物質がほとんどないということ)は、素粒子論におけるひとつの謎とされている。☆考察反物質の基本的な力は斥力であることから、重力・反重力の分離後(ビッグバンから10のマイナス44乗秒後)、反物質は物質よりも高速で拡散したと考えられる。【参 考】1. No.16 不確定性原理2.Jeff Miller, Ph.D.” Can Quantum Mechanics Produce a Universe from Nothing?”http://www.apologeticspress.org/apcontent.aspx?category=12&article=45843. 島根大学集中講義 真空の性質20094.Wikipedia:宇宙のインフレーション5. No.16-3 真空の相転移・インフレーション宇宙・トンネル効果6.Wikipedia:トンネル効果7. 前野昌弘 “量子力学入門" 20060216 (p.107) 8.三菱電機”宇宙創生時の急膨脹「インフレーション」の証拠写真を撮る日”9.「気が遠くなる未来の宇宙のはなし」佐藤勝彦(2013年刊)10.「宇宙が始まる前には何があったのか?」ローレンス・クラウス(2013年11月刊)11. 産経新聞 2016021212.Wikipedia:宇宙重力波望遠鏡13. LISA Project Office14.No.18 ビッグバン・モデル15.「宇宙は何でできているのか」村山 斉 (p.215)