21 Standard Theory(Standard Model) 【What is the Universe?】Dialogue with the Universe
[Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction(+Strong interaction
21-1 Overview
・Weinberg-Salam theory and quantumchromodynamics are the foundation of elementary particle physics, and are called standard theory or standard model.
・Standard theory is one of the theory for describing the three forces(electromagnetic force, weak force, strong force) in the same framework, but it is not a unified theory of the three forces.
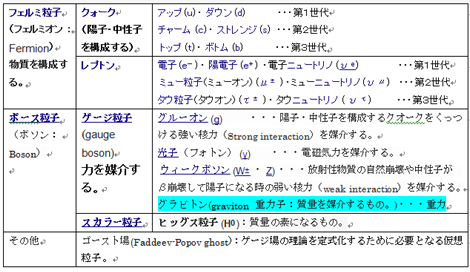
・Particles of the standard model consists(17 types)
Fermi particles(fermions) constituting a substance(12 types :quark and lepton)
Gauge particles that mediate the force(4)
Higgs particles comprising the mass of the element(1)
= Substance and force are made of elementary particles.
・Force occurs at the catch of Bose particles (bosons).
○ Standard model
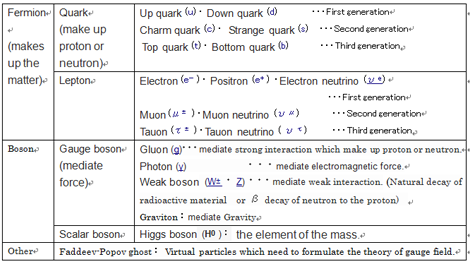
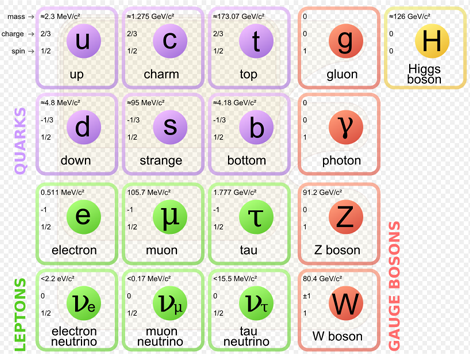
※The Standard Model of elementary particles (more schematic depiction), with the three generations of matter, gauge bosons in the fourth column, and the Higgs boson in the fifth.
MissMJ - Own work by uploader, PBS NOVA, Fermilab, Office of Science, United States Department of Energy, Particle Data Group [1]
※Generation: It is only say that lined the respective sets in light order of mass. Elementary particles of the second generation and later present at the time of creation of the universe, it is not present in the current global.
※Why the generation structure exists is one of the mysteries of the current elementary particle theory
※ Quarks make up hadrons (protons, neutrons), but do not have internal structure.
・Quark can not be observed unless a significant high-energy state, so its nature is not known yet well.
※The mass of the top quark is about 50 000 times the up quark. Weight of much gold atom.
※Neutrinos have tiny mass, and they are electrically neutral. So even met with other materials they pass through without reaction. The neutrino (meaning "little neutral one" in Italian) is denoted by the Greek letter ν (nu).
[Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction(+Strong interaction
21-1 Overview
・Weinberg-Salam theory and quantumchromodynamics are the foundation of elementary particle physics, and are called standard theory or standard model.
・Standard theory is one of the theory for describing the three forces(electromagnetic force, weak force, strong force) in the same framework, but it is not a unified theory of the three forces.
・Particles of the standard model consists(17 types)
Fermi particles(fermions) constituting a substance(12 types :quark and lepton)
Gauge particles that mediate the force(4)
Higgs particles comprising the mass of the element(1)
= Substance and force are made of elementary particles.
・Force occurs at the catch of Bose particles (bosons).
○ Standard model


※The Standard Model of elementary particles (more schematic depiction), with the three generations of matter, gauge bosons in the fourth column, and the Higgs boson in the fifth.
MissMJ - Own work by uploader, PBS NOVA, Fermilab, Office of Science, United States Department of Energy, Particle Data Group [1]
※Generation: It is only say that lined the respective sets in light order of mass. Elementary particles of the second generation and later present at the time of creation of the universe, it is not present in the current global.
※Why the generation structure exists is one of the mysteries of the current elementary particle theory
※ Quarks make up hadrons (protons, neutrons), but do not have internal structure.
・Quark can not be observed unless a significant high-energy state, so its nature is not known yet well.
※The mass of the top quark is about 50 000 times the up quark. Weight of much gold atom.
※Neutrinos have tiny mass, and they are electrically neutral. So even met with other materials they pass through without reaction. The neutrino (meaning "little neutral one" in Italian) is denoted by the Greek letter ν (nu).
- Because neutrions are particles having no electric charge, they may themselves are anti-particles like π-mesons. [Wikipedia]
※Bosons mediate force, and not follow the Pauli exclusion principle, and can be packed in the same place any number.
(Atoms are stuck in the electromagnetic force.)
(Electromagnetic force is transmitted by the particles exchange photons.)
※Pauli exclusion principle:The two Fermi particles can not occupy the same quantum state.
(The two Fermi particles, in limitations impose the uncertainty principle, both the position and velocity can not be the same.)
・・・If assuming that this world has been created without the exclusion principle, quark would not have shaped the separate clearly defined protons and neutrons. And, they would not also be shaping the atom. Substantially uniform density "soup" would be present.
※Strong interaction:Electromagnetic force: Weak interaction: Gravity
=1:10 to the power of minus 2 :10 to the power of minus 5:10 to the power of minus 40
※Strong nuclear force and the weak nuclear force works only at a distance less than the diameter of the nucleus.
※Weak force and the electromagnetic force was the same force immediately after the universe birth.
... Higgs particles are related to this symmetry breaking.
※Fermion (material particles) and bosons (particles of force) is replaced by the quantum theoretic dimension.
21-2 Tsaks
1) As a minimum unit of particle, the standard model considers "point" without size. The points can get closer to each other as much as possible, and calculating the value of gravity at that time makes the answer infinite, which is impossible in reality. This infinite problem is why the standard model can not incorporate gravity well. → String theory(Considering strings, you do not have to assume situations that produce infinite values.)
2)It is shown clearly that the dark matter occupies about 1/4 of the energy density of the universe. However, the particles which serve as a candidate of the dark matter do not exist in a standard model. Therefore, to ask elementary particle for the true character of the dark matter, extension of a standard model is required.
【Theory, etc.】
<Electromagnetic force, weak force ...>
1.Weinberg-Salam theory(WS theory) ,Electroweak unified theory (1967),
○This theory incorporates the idea of spontaneous symmetry breaking, and gives a mass in a natural way to gauge particles.
○In Weinberg-Salam theory, electromagnetic power and the weak power of appearing at the time of β disintegration[2] were unified by Gauge theory.
○According to gauge theory, the place, i.e. particles (gauge bosons) exists between the elementary particles which carry out an interaction.
○Gauge boson (weak boson (W boson, Z boson)) is mediating the weak power of collapsing a neutron (a radioactive decay and).
○In 1983, the accelerator of CERN in Geneva discovered W boson and Z boson.
※Gauge theory
○Gauge theory[3] is a type of field theory of quantum physics in which the Lagrangian (the difference between the kinetic energy and potential energy) is invariant. [4]・・・Extension of electromagnetism
・Gauge theory originates from the idea of Hermann Weyl in 1918.
・・・Gauge (measure) is given for each Spatio-Temporal point, and Lagrangian is decided so that the theory does not change even if the Spatio-Temporal point changes (gauge is kind of degrees of freedom, gauge freedom is gived so that the theory remain theoretically unchanged.)
(☆ Since kinetic energy is expressed by a negative, "difference" is the sum of the two energies.)
1) In Quantum Field Theory, fields form particles, and particles form fields, and particles are medium to convey the power of fields.
(As an example electromagnetic force acting between the electrons is caused by the exchange of photons. W and Z bosons mediate the weak force, gluons mediate the strong force. )[5]
※Three of the four forces of nature (electromagnetic force, weak force, strong force) are grouped by gauge theory.
2) Moreover, in a vacuum, the amount of the field is slightly vibrate. Complete "Void" does not exist. [5]
2. Cabibbo–Kobayashi–Maskawa matrix (1973), etc [6]
○ CP violation
If quarks are three generations, it can theoretically explain the CP violation.
← 3 is required for the CP symmetry is broken.
⇒ By CP violation, the matter is leaving without annihilation with particles (matter) and antiparticles (antimatter).
※ P: Parity Symmetry: In quantum physics, a parity transformation (also called parity inversion) is the flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate. That no physical laws change by switching right and left or up and down, is referred to as parity symmetry
※ C: Charge symmetry: Symmetry of particles and antiparticles. If C-symmetry is maintained, it can be converted between particles and antiparticles. Electromagnetism, gravity and the strong interaction all obey C-symmetry, but weak interactions violate C-symmetry.
○Matter and antimatter: asymmetry of one billionth [7]
・In today's universe, for one proton, there are approximately one billion photons as the cosmic microwave background radiation.These photons are the leftovers of pair annihilation, immediately after the universe birth, of matter and antimatter.
・This process is not fully understood. The nature of the world of the micro is still poorly understood.
< Strong force>
1. Quantum chromodynamics, QCD late 1970s
・Since neutron without electric charge has the strong magnetic moment, physicists was forced to assume that hadron (proton, neutron) is constituted with smaller element.
・Now, hadron is considered as what consists of six kinds of quarks, and eight kinds of gluons which mediate strong interaction inside hadron.
・There are 3 colorred quarks,red, blue and green, and a white hadron will be formed if the three joins together.
・The word "color" is what imagined the three primary colors of light and was used figuratively.
< Other quark Related>
• It is not possible to retrieve the quark in monochromatic.
・Quark is an energy, there is no form to quark.
・Quarks can be packed in the same place. (Do not follow the Pauli exclusion principle.)
・Quark produce a strong force by replacing the "color" (:Ironi:Bose particles = gluon).
・The force becomes stronger as the distance leaves.
・Placing the electrons of high energy protons, the force is weakened. And Quark is I appear to move.
○ The use of antimatter: PET (positron emission tomography)
・Positron is the antimatter of electron.
・Positron changes in energy by collisions with electron. We observe this energy as photon.
・A PET scan uses a small amount of radioactive material (tracer).
・It is possible to detect a rise in glucose metabolism levels in the tumor tissue by its tracer emits positrons.
【References】
1. Matter - Wikipedia
2. In the changing process of neutron to the proton, electron (beta ray (β ray)) is released.
3. Gauge theory - Wikipedia
4. ラグランジュ力学 - Wikipedia
5. 場の量子論 - Wikipedia
6. Kobayashi–Maskawa matrix - Wikipedia
7. Lawrence M. Krauss “A Universe from Nothing” 2012
【Change log】
20170510 Organization of tasks
(Atoms are stuck in the electromagnetic force.)
(Electromagnetic force is transmitted by the particles exchange photons.)
※Pauli exclusion principle:The two Fermi particles can not occupy the same quantum state.
(The two Fermi particles, in limitations impose the uncertainty principle, both the position and velocity can not be the same.)
・・・If assuming that this world has been created without the exclusion principle, quark would not have shaped the separate clearly defined protons and neutrons. And, they would not also be shaping the atom. Substantially uniform density "soup" would be present.
※Strong interaction:Electromagnetic force: Weak interaction: Gravity
=1:10 to the power of minus 2 :10 to the power of minus 5:10 to the power of minus 40
※Strong nuclear force and the weak nuclear force works only at a distance less than the diameter of the nucleus.
※Weak force and the electromagnetic force was the same force immediately after the universe birth.
... Higgs particles are related to this symmetry breaking.
※Fermion (material particles) and bosons (particles of force) is replaced by the quantum theoretic dimension.
21-2 Tsaks
1) As a minimum unit of particle, the standard model considers "point" without size. The points can get closer to each other as much as possible, and calculating the value of gravity at that time makes the answer infinite, which is impossible in reality. This infinite problem is why the standard model can not incorporate gravity well. → String theory(Considering strings, you do not have to assume situations that produce infinite values.)
2)It is shown clearly that the dark matter occupies about 1/4 of the energy density of the universe. However, the particles which serve as a candidate of the dark matter do not exist in a standard model. Therefore, to ask elementary particle for the true character of the dark matter, extension of a standard model is required.
【Theory, etc.】
<Electromagnetic force, weak force ...>
1.Weinberg-Salam theory(WS theory) ,Electroweak unified theory (1967),
○This theory incorporates the idea of spontaneous symmetry breaking, and gives a mass in a natural way to gauge particles.
○In Weinberg-Salam theory, electromagnetic power and the weak power of appearing at the time of β disintegration[2] were unified by Gauge theory.
○According to gauge theory, the place, i.e. particles (gauge bosons) exists between the elementary particles which carry out an interaction.
○Gauge boson (weak boson (W boson, Z boson)) is mediating the weak power of collapsing a neutron (a radioactive decay and).
○In 1983, the accelerator of CERN in Geneva discovered W boson and Z boson.
※Gauge theory
○Gauge theory[3] is a type of field theory of quantum physics in which the Lagrangian (the difference between the kinetic energy and potential energy) is invariant. [4]・・・Extension of electromagnetism
・Gauge theory originates from the idea of Hermann Weyl in 1918.
・・・Gauge (measure) is given for each Spatio-Temporal point, and Lagrangian is decided so that the theory does not change even if the Spatio-Temporal point changes (gauge is kind of degrees of freedom, gauge freedom is gived so that the theory remain theoretically unchanged.)
(☆ Since kinetic energy is expressed by a negative, "difference" is the sum of the two energies.)
1) In Quantum Field Theory, fields form particles, and particles form fields, and particles are medium to convey the power of fields.
(As an example electromagnetic force acting between the electrons is caused by the exchange of photons. W and Z bosons mediate the weak force, gluons mediate the strong force. )[5]
※Three of the four forces of nature (electromagnetic force, weak force, strong force) are grouped by gauge theory.
2) Moreover, in a vacuum, the amount of the field is slightly vibrate. Complete "Void" does not exist. [5]
2. Cabibbo–Kobayashi–Maskawa matrix (1973), etc [6]
○ CP violation
If quarks are three generations, it can theoretically explain the CP violation.
← 3 is required for the CP symmetry is broken.
⇒ By CP violation, the matter is leaving without annihilation with particles (matter) and antiparticles (antimatter).
※ P: Parity Symmetry: In quantum physics, a parity transformation (also called parity inversion) is the flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate. That no physical laws change by switching right and left or up and down, is referred to as parity symmetry
※ C: Charge symmetry: Symmetry of particles and antiparticles. If C-symmetry is maintained, it can be converted between particles and antiparticles. Electromagnetism, gravity and the strong interaction all obey C-symmetry, but weak interactions violate C-symmetry.
○Matter and antimatter: asymmetry of one billionth [7]
・In today's universe, for one proton, there are approximately one billion photons as the cosmic microwave background radiation.These photons are the leftovers of pair annihilation, immediately after the universe birth, of matter and antimatter.
・This process is not fully understood. The nature of the world of the micro is still poorly understood.
< Strong force>
1. Quantum chromodynamics, QCD late 1970s
・Since neutron without electric charge has the strong magnetic moment, physicists was forced to assume that hadron (proton, neutron) is constituted with smaller element.
・Now, hadron is considered as what consists of six kinds of quarks, and eight kinds of gluons which mediate strong interaction inside hadron.
・There are 3 colorred quarks,red, blue and green, and a white hadron will be formed if the three joins together.
・The word "color" is what imagined the three primary colors of light and was used figuratively.
< Other quark Related>
• It is not possible to retrieve the quark in monochromatic.
・Quark is an energy, there is no form to quark.
・Quarks can be packed in the same place. (Do not follow the Pauli exclusion principle.)
・Quark produce a strong force by replacing the "color" (:Ironi:Bose particles = gluon).
・The force becomes stronger as the distance leaves.
・Placing the electrons of high energy protons, the force is weakened. And Quark is I appear to move.
○ The use of antimatter: PET (positron emission tomography)
・Positron is the antimatter of electron.
・Positron changes in energy by collisions with electron. We observe this energy as photon.
・A PET scan uses a small amount of radioactive material (tracer).
・It is possible to detect a rise in glucose metabolism levels in the tumor tissue by its tracer emits positrons.
【References】
1. Matter - Wikipedia
2. In the changing process of neutron to the proton, electron (beta ray (β ray)) is released.
3. Gauge theory - Wikipedia
4. ラグランジュ力学 - Wikipedia
5. 場の量子論 - Wikipedia
6. Kobayashi–Maskawa matrix - Wikipedia
7. Lawrence M. Krauss “A Universe from Nothing” 2012
【Change log】
20170510 Organization of tasks